"렘니스케이트(lemniscate) 곡선의 길이와 타원적분"의 두 판 사이의 차이
(피타고라스님이 이 페이지의 이름을 렘니스케이트(lemniscate) 곡선의 길이와 타원적분로 바꾸었습니다.) |
Pythagoras0 (토론 | 기여) |
||
| (사용자 2명의 중간 판 28개는 보이지 않습니다) | |||
| 1번째 줄: | 1번째 줄: | ||
| − | + | ==개요== | |
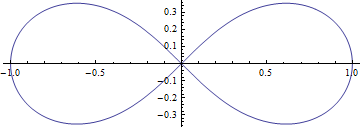
| − | + | [[파일:렘니스케이트(lemniscate) 곡선의 길이와 타원적분1.png]] | |
| − | + | * 극좌표계에서 방정식 <math>r^2=\cos2\theta</math> 로 주어진 곡선을 베르누이의 렘니스케이트 곡선이라 부름. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * 극좌표계에서 | ||
* 카테시안 좌표계에서는 <math>(x^2 + y^2)^2=x^2 - y^2</math>로 주어진다 | * 카테시안 좌표계에서는 <math>(x^2 + y^2)^2=x^2 - y^2</math>로 주어진다 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==렘니스케이트 곡선의 둘레의 길이와 타원적분== | |
| + | ;정리 | ||
| + | 렘니스케이트 곡선의 둘레의 길이 <math>L</math>은 [[타원적분]]으로 표현되며 다음이 성립한다 | ||
| + | :<math>L=4\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^4}}=2\sqrt{2}K(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}})=5.2441\cdots</math> | ||
| + | 여기서 <math>K</math>는 [[제1종타원적분 K (complete elliptic integral of the first kind)]] | ||
| + | :<math>K(k) = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \frac{d\theta}{\sqrt{1-k^2 \sin^2\theta}}.</math> | ||
| + | 또한 다음이 성립한다 | ||
| + | :<math>L=B(1/2,1/4)=\frac{\Gamma(\frac{1}{2})\Gamma(\frac{1}{4})}{\Gamma(\frac{3}{4})}=\frac{\Gamma(1/4)^2}{\sqrt{2\pi}}</math> | ||
| + | 여기서 <math>B</math>는 [[오일러 베타적분(베타함수)]]이고, <math>\Gamma</math>는 [[감마함수]] | ||
| − | < | + | ;증명 |
| + | 렘니스케이트 곡선은 <math>x=r(\theta)\cos\theta,y=r(\theta)\sin\theta</math>로 매개화되며, 다음을 확인할 수 있다 | ||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | r'(\theta)=-\frac{\sin 2\theta}{r(\theta)} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | 매개화를 이용하여, 둘레의 길이를 계산하면 다음을 얻는다 | ||
| + | :<math>L=4\int_{0}^{\pi/4}\sqrt{r'(\theta)^2+r(\theta)^2}\,d\theta=4\int_{0}^{\pi/4}\sqrt{\frac{\sin^2 2\theta}{r^2(\theta)}+r^2(\theta)}\,d\theta=4\int_{0}^{\pi/4}\frac{1}{\sqrt{\cos 2\theta}}\,d\theta</math> | ||
| + | 이 때, <math>\cos 2\theta=\cos^2{\phi}</math> 를 이용하여 치환하면, | ||
| + | :<math>d\theta=\frac{\sin\phi\cos\phi}{\sqrt{1-\cos^4\phi}}\,d\phi=\frac{\cos\phi}{\sqrt{1+\cos^2\phi}}\,d\phi,</math> | ||
| + | :<math>L=4\int_0^{\pi/2}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\cos^2 \phi}}\,d\phi=2\sqrt{2}\int_0^{\pi/2}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{1}{2}\sin^2 \phi}}\,d\phi \label{eq1}</math> | ||
| + | \ref{eq1}로부터 다음을 얻는다 | ||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | L=2\sqrt{2}K(1/\sqrt{2}) | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | \ref{eq1}에서 <math>x=\cos\phi</math>로 치환하면, | ||
| + | :<math>L=4\int_0^{\pi/2}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\cos^2 \phi}}\,d\phi=4\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^4}}=B(1/2,1/4)=\frac{\Gamma(\frac{1}{2})\Gamma(\frac{1}{4})}{\Gamma(\frac{3}{4})}=\frac{\Gamma(1/4)^2}{\sqrt{2\pi}}=5.2441</math> | ||
| + | ■ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==가우스의 렘니스케이트 상수== | |
| + | * 렘니스케이트 상수 <math>\omega</math>를 다음과 같이 정의 | ||
| + | :<math>\omega:=2\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^4}}=2.62\cdots</math> | ||
| + | * 수론적 성질에 대해서는 [[가우스의 렘니스케이트 상수]] 항목 참조 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==재미있는 사실== | |
| − | * [[ | + | * 곡선의 모양이 무한대 기호와 같음 |
| + | * 무한대는 그 한계가 없기에 리본을 뜻하는 'lemniscus'라는 말로 불릴 때도 있었으며, 그 때문에 무한대 기호가 누운 8자 모양이 되었다는 설이 있음 | ||
| + | [[파일:렘니스케이트 반지.png|300px]] | ||
| − | + | ==역사== | |
| + | * http://www.gormagon.org/2005/04/17/the-lemniscate-infinity-symbol/ | ||
| + | * 1684 베르누이 'Acta Eruditorum' | ||
| + | * 18세기 파그나노, 오일러, 르장드르의 타원적분 연구 | ||
| + | * 1798~1799년 가우스가 <math>\pi/\omega</math>가 1과 <math>\sqrt2</math>의 [[산술 기하 평균 (arithmetic-geometric mean)]]이 됨을 관찰 | ||
| + | * [[수학사 연표]] | ||
| − | * | + | ==관련된 항목들== |
| + | * [[산술기하평균함수(AGM)와 파이값의 계산]] | ||
| + | * [[타원곡선의 주기]] | ||
| + | * [[Chowla-셀베르그 공식]] | ||
| + | * [[무리수와 초월수]] | ||
| + | * [[아이젠슈타인 기약다항식 판정법]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==수학용어번역== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* [http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en%7Cko&q=lemniscate http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en|ko&q=lemniscate] | * [http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en%7Cko&q=lemniscate http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en|ko&q=lemniscate] | ||
| − | * Latin | + | * Latin lemniscus meaning "ribbon" |
| − | * | + | * 번역용어제안 |
** 쌍타원, 겹타원, 이중타원, 나비리본 | ** 쌍타원, 겹타원, 이중타원, 나비리본 | ||
| − | ** '베르누이의 연주형'(lemniscate) | + | ** '베르누이의 연주형'(lemniscate) [http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=ko%7Cko&q=%EC%97%B0%EC%A3%BC http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=ko|ko&q=연주] |
| − | * | + | * {{수학용어집|url=lemniscate}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==매스매티카 파일 및 계산 리소스== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
* https://docs.google.com/leaf?id=0B8XXo8Tve1cxZjRmZjkwMjgtNGY0Mi00MzllLWExMGQtZjExZjIzZWMyNDRk&sort=name&layout=list&num=50 | * https://docs.google.com/leaf?id=0B8XXo8Tve1cxZjRmZjkwMjgtNGY0Mi00MzllLWExMGQtZjExZjIzZWMyNDRk&sort=name&layout=list&num=50 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==사전 형태의 자료== | |
| − | + | * http://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/렘니스케이트 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/lemniscate | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/lemniscate | ||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infinity | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infinity | ||
| − | * | + | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gauss's_constant |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==관련도서== | |
| + | * Mathematics by experiment: plausible reasoning in the 21st century | ||
| + | ** M. Borwein and D. H. Bailey, , A K Peters, Natick, MA, 2003. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==리뷰, 에세이, 강의노트== | |
| − | + | * [http://www.ias.ac.in/resonance/Apr2004/Apr2004p21-29.htm From Lintearia to Lemniscate I : physics to mathematics] R Sridharan | |
| − | + | * [http://www.ias.ac.in/resonance/June2004/June2004p11-20.html From Lintearia to Lemniscate II: Gauss and Landen’s Work] R Sridharan | |
| − | * | + | * [http://www.springerlink.com/content/t32h69374h887w33/ The Lemniscate and Fagnano's Contributions to Elliptic Integrals]Raymond Ayoub, Archive for History of Exact Sciences, 1984 |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[분류:곡선]] | |
| + | [[분류:타원적분]] | ||
| − | + | ==메타데이터== | |
| − | + | ===위키데이터=== | |
| − | + | * ID : [https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q10545374 Q10545374] | |
| − | + | ===Spacy 패턴 목록=== | |
| − | * [ | + | * [{'LEMMA': 'lemniscate'}] |
| − | |||
| − | * [ | ||
2021년 2월 17일 (수) 04:04 기준 최신판
개요
- 극좌표계에서 방정식 \(r^2=\cos2\theta\) 로 주어진 곡선을 베르누이의 렘니스케이트 곡선이라 부름.
- 카테시안 좌표계에서는 \((x^2 + y^2)^2=x^2 - y^2\)로 주어진다
렘니스케이트 곡선의 둘레의 길이와 타원적분
- 정리
렘니스케이트 곡선의 둘레의 길이 \(L\)은 타원적분으로 표현되며 다음이 성립한다 \[L=4\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^4}}=2\sqrt{2}K(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}})=5.2441\cdots\] 여기서 \(K\)는 제1종타원적분 K (complete elliptic integral of the first kind) \[K(k) = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \frac{d\theta}{\sqrt{1-k^2 \sin^2\theta}}.\] 또한 다음이 성립한다 \[L=B(1/2,1/4)=\frac{\Gamma(\frac{1}{2})\Gamma(\frac{1}{4})}{\Gamma(\frac{3}{4})}=\frac{\Gamma(1/4)^2}{\sqrt{2\pi}}\] 여기서 \(B\)는 오일러 베타적분(베타함수)이고, \(\Gamma\)는 감마함수
- 증명
렘니스케이트 곡선은 \(x=r(\theta)\cos\theta,y=r(\theta)\sin\theta\)로 매개화되며, 다음을 확인할 수 있다 \[ r'(\theta)=-\frac{\sin 2\theta}{r(\theta)} \] 매개화를 이용하여, 둘레의 길이를 계산하면 다음을 얻는다 \[L=4\int_{0}^{\pi/4}\sqrt{r'(\theta)^2+r(\theta)^2}\,d\theta=4\int_{0}^{\pi/4}\sqrt{\frac{\sin^2 2\theta}{r^2(\theta)}+r^2(\theta)}\,d\theta=4\int_{0}^{\pi/4}\frac{1}{\sqrt{\cos 2\theta}}\,d\theta\] 이 때, \(\cos 2\theta=\cos^2{\phi}\) 를 이용하여 치환하면, \[d\theta=\frac{\sin\phi\cos\phi}{\sqrt{1-\cos^4\phi}}\,d\phi=\frac{\cos\phi}{\sqrt{1+\cos^2\phi}}\,d\phi,\] \[L=4\int_0^{\pi/2}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\cos^2 \phi}}\,d\phi=2\sqrt{2}\int_0^{\pi/2}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{1}{2}\sin^2 \phi}}\,d\phi \label{eq1}\] \ref{eq1}로부터 다음을 얻는다 \[ L=2\sqrt{2}K(1/\sqrt{2}) \] \ref{eq1}에서 \(x=\cos\phi\)로 치환하면, \[L=4\int_0^{\pi/2}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\cos^2 \phi}}\,d\phi=4\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^4}}=B(1/2,1/4)=\frac{\Gamma(\frac{1}{2})\Gamma(\frac{1}{4})}{\Gamma(\frac{3}{4})}=\frac{\Gamma(1/4)^2}{\sqrt{2\pi}}=5.2441\] ■
가우스의 렘니스케이트 상수
- 렘니스케이트 상수 \(\omega\)를 다음과 같이 정의
\[\omega:=2\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^4}}=2.62\cdots\]
- 수론적 성질에 대해서는 가우스의 렘니스케이트 상수 항목 참조
재미있는 사실
- 곡선의 모양이 무한대 기호와 같음
- 무한대는 그 한계가 없기에 리본을 뜻하는 'lemniscus'라는 말로 불릴 때도 있었으며, 그 때문에 무한대 기호가 누운 8자 모양이 되었다는 설이 있음
역사
- http://www.gormagon.org/2005/04/17/the-lemniscate-infinity-symbol/
- 1684 베르누이 'Acta Eruditorum'
- 18세기 파그나노, 오일러, 르장드르의 타원적분 연구
- 1798~1799년 가우스가 \(\pi/\omega\)가 1과 \(\sqrt2\)의 산술 기하 평균 (arithmetic-geometric mean)이 됨을 관찰
- 수학사 연표
관련된 항목들
수학용어번역
- http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en|ko&q=lemniscate
- Latin lemniscus meaning "ribbon"
- 번역용어제안
- 쌍타원, 겹타원, 이중타원, 나비리본
- '베르누이의 연주형'(lemniscate) http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=ko|ko&q=연주
- lemniscate - 대한수학회 수학용어집
매스매티카 파일 및 계산 리소스
사전 형태의 자료
- http://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/렘니스케이트
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/lemniscate
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infinity
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gauss's_constant
관련도서
- Mathematics by experiment: plausible reasoning in the 21st century
- M. Borwein and D. H. Bailey, , A K Peters, Natick, MA, 2003.
리뷰, 에세이, 강의노트
- From Lintearia to Lemniscate I : physics to mathematics R Sridharan
- From Lintearia to Lemniscate II: Gauss and Landen’s Work R Sridharan
- The Lemniscate and Fagnano's Contributions to Elliptic IntegralsRaymond Ayoub, Archive for History of Exact Sciences, 1984
메타데이터
위키데이터
- ID : Q10545374
Spacy 패턴 목록
- [{'LEMMA': 'lemniscate'}]