"루트 시스템 (root system)과 딘킨 다이어그램 (Dynkin diagram)"의 두 판 사이의 차이
Pythagoras0 (토론 | 기여) |
|||
| (사용자 2명의 중간 판 12개는 보이지 않습니다) | |||
| 1번째 줄: | 1번째 줄: | ||
| − | + | ==개요== | |
| − | * [[ | + | * 루트 시스템은 유한차원 유클리드 벡터공간에서 여러가지 조건들을 만족시키는 벡터들의 모임이다 |
| + | ** non-zero eigenvalues of Cartan subalgebra | ||
| + | * [[리군과 리대수]]의 분류, 격자의 분류, [[유한반사군과 콕세터군(finite reflection groups and Coxeter groups)]] 등에서 중요하게 활용 | ||
| + | * 딘킨 다이어그램은 루트 시스템을 표현하는 그래프이다 | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==정의== | |
| − | * | + | * E를 [[내적공간|내적]]이 주어진 유클리드 벡터공간이라 하자. |
| − | + | * 다음 조건을 만족시키는 E의 유한인 부분집합 <math>\Phi</math>를 루트 시스템이라 한다. | |
| − | + | ** <math>\Phi</math>는 E를 스팬(span)하며 <math>0 \not \in \Phi</math> | |
| − | + | ** (reduced) <math>\alpha \in \Phi</math>, <math>\lambda \alpha \in \Phi \iff \lambda=\pm 1</math> | |
| − | + | ** <math>\alpha,\beta \in \Phi</math>이면 <math>\sigma_\alpha(\beta) =\beta-2\frac{(\beta,\alpha)}{(\alpha,\alpha)}\alpha \in \Phi</math> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * 다음 조건을 | ||
| − | ** | ||
| − | ** (reduced) <math>\alpha \in \Phi</math>, | ||
| − | ** <math>\alpha,\beta \in \Phi</math> | ||
** <math>\langle \beta, \alpha \rangle = 2 \frac{(\beta,\alpha)}{(\alpha,\alpha)} \in \mathbb{Z}</math> | ** <math>\langle \beta, \alpha \rangle = 2 \frac{(\beta,\alpha)}{(\alpha,\alpha)} \in \mathbb{Z}</math> | ||
| − | * 마지막 | + | * 마지막 조건을 crystallographic 또는 integrality 조건이라 한다 |
| − | * a subgroup | + | * a subgroup of <math>GL(V)</math> is crystallographic if it stabilizes a lattice L in V |
| − | * e.g. the Weyl | + | * e.g. the Weyl group of a Lie algebra stabilizes the root lattice or the weight lattice |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==딘킨 다이어그램 (Dynkin diagram)== | ||
* first draw the simple roots as nodes | * first draw the simple roots as nodes | ||
| − | * | + | * draw <math>4(e_i, e_j)^2</math>lines for two roots <math>e_i, e_j</math> |
| + | * <math>\frac{\pi}{2}</math> , <math>\frac{\pi}{3}</math>, <math>\frac{\pi}{4}</math>, <math>\frac{\pi}{6}</math> 0,1,2,3 lines | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==2차원 루트 시스템의 분류== | |
| − | * <math>A_1\times A_1</math>, | + | * <math>A_1\times A_1</math>, <math>A_2</math>, <math>B_2</math>, <math>G_2</math> |
A1 x A1 | A1 x A1 | ||
| 70번째 줄: | 54번째 줄: | ||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Root_system ] | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Root_system ] | ||
| − | [ | + | [[파일:2696052-MSP45719773453e5409bcd000043c1iebh17cda58g.gif]] |
| − | [ | + | [[파일:2696052-MSP402197733f5dbe80g5d000056hb767e4digb412.gif]] |
| − | [ | + | [[파일:2696052-MSP132719772cfcfe659i75000064ieda8fh9d30h5e.gif]] |
| − | [ | + | [[파일:2696052-MSP98119772g2ig5gid8he000031i1h30a8gacdi00.gif]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==ADE 의 분류== | |
(0) G cannot contain affine A_n, D_n, E_n | (0) G cannot contain affine A_n, D_n, E_n | ||
| 92번째 줄: | 76번째 줄: | ||
(2) G has \leq 1 branch point (does not contain affine D_5, D_6,D_7, ) | (2) G has \leq 1 branch point (does not contain affine D_5, D_6,D_7, ) | ||
| − | (3) | + | (3) branch point has order \leq 3 (affine D_4) What are length of legs of G? |
Leg of length 0 -> G=A_n | Leg of length 0 -> G=A_n | ||
| 102번째 줄: | 86번째 줄: | ||
so one leg has length 1 | so one leg has length 1 | ||
| − | 2 legs of length 1 : | + | 2 legs of length 1 : G is D_n |
so can assume 2 other legs have length \geq 2 | so can assume 2 other legs have length \geq 2 | ||
| 114번째 줄: | 98번째 줄: | ||
So G is E6,E7, E8 | So G is E6,E7, E8 | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
일반적인 경우 | 일반적인 경우 | ||
| − | * how | + | * how to classify all connected admissible diagrams |
** subdiagram is also admissible | ** subdiagram is also admissible | ||
** there are at most (n-1) pairs of nodes | ** there are at most (n-1) pairs of nodes | ||
| 128번째 줄: | 112번째 줄: | ||
** study double lines and triple nodes | ** study double lines and triple nodes | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==reflection groups== | |
| − | + | * B_n, C_n, BC_n -> same reflection group (Z/nZ).S_n | |
| + | * | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==역사== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&tbs=tl:1&q= | * http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&tbs=tl:1&q= | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[수학사 연표]] |
| − | * | + | * |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==메모== | |
| − | + | * <math>\bullet - \bullet</math> | |
| − | * <math>\bullet - \bullet</math | ||
* http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/2DRootSystems/ | * http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/2DRootSystems/ | ||
* reflection groups | * reflection groups | ||
| 190번째 줄: | 152번째 줄: | ||
* Platonic Solids | * Platonic Solids | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==관련된 항목들== | |
| + | * [[리군과 리대수]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==매스매티카 파일 및 계산 리소스== | |
| − | + | * https://docs.google.com/file/d/0B8XXo8Tve1cxWTU1UnRqVlRrZ00/edit | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==사전 형태의 자료== | ||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/root_systems | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/root_systems | ||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dynkin_diagram | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dynkin_diagram | ||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coxeter_number | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coxeter_number | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==관련논문== | |
| + | * [http://www.jstor.org/stable/2324217 Two Amusing Dynkin Diagram Graph Classifications] Robert A. Proctor, <cite>The American Mathematical Monthly</cite>, Vol. 100, No. 10 (Dec., 1993), pp. 937-941 | ||
| + | [[분류:리군과 리대수]] | ||
| − | * [ | + | ==메타데이터== |
| − | + | ===위키데이터=== | |
| − | * | + | * ID : [https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q534131 Q534131] |
| − | + | ===Spacy 패턴 목록=== | |
| + | * [{'LOWER': 'root'}, {'LEMMA': 'system'}] | ||
2021년 2월 17일 (수) 04:41 기준 최신판
개요
- 루트 시스템은 유한차원 유클리드 벡터공간에서 여러가지 조건들을 만족시키는 벡터들의 모임이다
- non-zero eigenvalues of Cartan subalgebra
- 리군과 리대수의 분류, 격자의 분류, 유한반사군과 콕세터군(finite reflection groups and Coxeter groups) 등에서 중요하게 활용
- 딘킨 다이어그램은 루트 시스템을 표현하는 그래프이다
정의
- E를 내적이 주어진 유클리드 벡터공간이라 하자.
- 다음 조건을 만족시키는 E의 유한인 부분집합 \(\Phi\)를 루트 시스템이라 한다.
- \(\Phi\)는 E를 스팬(span)하며 \(0 \not \in \Phi\)
- (reduced) \(\alpha \in \Phi\), \(\lambda \alpha \in \Phi \iff \lambda=\pm 1\)
- \(\alpha,\beta \in \Phi\)이면 \(\sigma_\alpha(\beta) =\beta-2\frac{(\beta,\alpha)}{(\alpha,\alpha)}\alpha \in \Phi\)
- \(\langle \beta, \alpha \rangle = 2 \frac{(\beta,\alpha)}{(\alpha,\alpha)} \in \mathbb{Z}\)
- 마지막 조건을 crystallographic 또는 integrality 조건이라 한다
- a subgroup of \(GL(V)\) is crystallographic if it stabilizes a lattice L in V
- e.g. the Weyl group of a Lie algebra stabilizes the root lattice or the weight lattice
딘킨 다이어그램 (Dynkin diagram)
- first draw the simple roots as nodes
- draw \(4(e_i, e_j)^2\)lines for two roots \(e_i, e_j\)
- \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) , \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), \(\frac{\pi}{4}\), \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) 0,1,2,3 lines
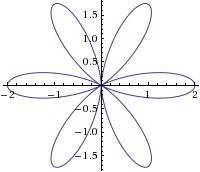
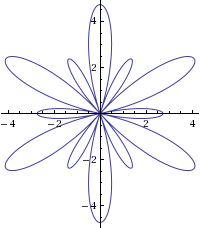
2차원 루트 시스템의 분류
- \(A_1\times A_1\), \(A_2\), \(B_2\), \(G_2\)
A1 x A1
http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=r%3D1%2Bcos+(4theta)
A2
http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=r%3D1%2B+cos+(6theta)
B2
http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=r%3D1-+(sqrt2+%2B1)^2+cos+(4theta)
G2
http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=r%3D1-(sqrt+3+%2B1)^2cos+(6theta)/2
ADE 의 분류
(0) G cannot contain affine A_n, D_n, E_n
(1) G is a tree (contains no cycles = affine A_n)
(2) G has \leq 1 branch point (does not contain affine D_5, D_6,D_7, )
(3) branch point has order \leq 3 (affine D_4) What are length of legs of G?
Leg of length 0 -> G=A_n
so assume legs have length \geq 1
(4) Not all legs have length \geq 2 : cannot contain affine E_6
so one leg has length 1
2 legs of length 1 : G is D_n
so can assume 2 other legs have length \geq 2
(5) cannot have 2 legs length \geq 3 because of affine E_7
So G has 1 leg length 1, 1 of length 2, one of length \geq 2
length is \leq 4, as G does not contain affine E_8
So G is E6,E7, E8
일반적인 경우
- how to classify all connected admissible diagrams
- subdiagram is also admissible
- there are at most (n-1) pairs of nodes
- no node has more than 3 lines
- study double lines and triple nodes
reflection groups
- B_n, C_n, BC_n -> same reflection group (Z/nZ).S_n
역사
메모
- \(\bullet - \bullet\)
- http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/2DRootSystems/
- reflection groups
- lie algebras
- Lie groups
- algebraic groups
- surfaces singularities
- quiver
- Platonic Solids
관련된 항목들
매스매티카 파일 및 계산 리소스
사전 형태의 자료
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/root_systems
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dynkin_diagram
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coxeter_number
관련논문
- Two Amusing Dynkin Diagram Graph Classifications Robert A. Proctor, The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 100, No. 10 (Dec., 1993), pp. 937-941
메타데이터
위키데이터
- ID : Q534131
Spacy 패턴 목록
- [{'LOWER': 'root'}, {'LEMMA': 'system'}]