"최단시간강하곡선 문제(Brachistochrone problem)"의 두 판 사이의 차이
Pythagoras0 (토론 | 기여) (→메타데이터: 새 문단) |
|||
| (사용자 2명의 중간 판 24개는 보이지 않습니다) | |||
| 1번째 줄: | 1번째 줄: | ||
| − | + | ==개요== | |
| − | * [[ | + | * 중력을 받고 있는 물체가 정지상태에서 출발하여 가장 짧은 시간내에 하강하기 위해서 따라야 하는 곡선 |
| + | * 1697년에 베르누이에 의하여 답이 출판 | ||
| + | [[파일:4402517-ParabNickF.gif]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [http://books.google.com/books?id=dptKVr-5LJAC&pg=PA223&sig=PVA7Q1U_MyXinobyhOf54BwjShQ&hl=en#v=onepage&q&f=false Classical Mechanics] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [http://books.google.com/books?id=dptKVr-5LJAC&pg=PA223&sig=PVA7Q1U_MyXinobyhOf54BwjShQ&hl=en#v=onepage&q&f=false ] | ||
곡선의 시작점을 <math>(x_0,y_0)=(0,0)</math>, 끝점을 <math>(x_1,y_1)</math>라 두자. | 곡선의 시작점을 <math>(x_0,y_0)=(0,0)</math>, 끝점을 <math>(x_1,y_1)</math>라 두자. | ||
| 24번째 줄: | 15번째 줄: | ||
<math>t=\int \frac{1}{v} \, ds</math>(v는 속력, ds 는 길이요소, t는 시간) | <math>t=\int \frac{1}{v} \, ds</math>(v는 속력, ds 는 길이요소, t는 시간) | ||
| − | 에너지 보존 법칙 <math>mgy=\frac{1}{2}mv^2</math> | + | 에너지 보존 법칙 <math>mgy=\frac{1}{2}mv^2</math> 에서<math>v=\sqrt{2gy}</math>. |
이제 곡선의 x좌표를 y의 함수로 생각하자. 곡선을 따라 내려올 때 걸리는 시간은 | 이제 곡선의 x좌표를 y의 함수로 생각하자. 곡선을 따라 내려올 때 걸리는 시간은 | ||
| − | + | :<math>T=\int \frac{1}{v} \, ds=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2g}}\int_{0}^{y} \frac{\sqrt{1+x'(y)^2}}{\sqrt{y}} \, dy</math> | |
| − | <math>T=\int \frac{1}{v} \, ds=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2g}}\int_{0}^{y} \frac{\sqrt{1+x'(y)^2}}{\sqrt{y}} \, dy</math> | ||
문제의 정의에 따라 이 적분값을 최소가 되게 하는 곡선을 찾아야 한다. | 문제의 정의에 따라 이 적분값을 최소가 되게 하는 곡선을 찾아야 한다. | ||
| − | <math>F(y,x,x')=\frac{\sqrt{1+(x')^2}}{\sqrt{y}}</math> | + | <math>F(y,x,x')=\frac{\sqrt{1+(x')^2}}{\sqrt{y}}</math> 에 대하여 [[오일러-라그랑지 방정식]] 을 적용하면, |
| − | + | :<math>0 =\frac{\partial F}{\partial x} - \frac{d}{dy} \frac{\partial F}{\partial x'}=-\frac{d}{dy}(\frac{x'(y)}{\sqrt{y(1+x'(y)^2)}})</math> | |
| − | <math>0 =\frac{\partial F}{\partial x} - \frac{d}{dy} \frac{\partial F}{\partial x'}=-\frac{d}{dy}(\frac{x'(y)}{\sqrt{y(1+x'(y)^2)}})</math> | ||
적당한 상수 a에 대하여 <math>\frac{x'(y)}{\sqrt{y(1+x'(y)^2)}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2a}}</math>라 두자. | 적당한 상수 a에 대하여 <math>\frac{x'(y)}{\sqrt{y(1+x'(y)^2)}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2a}}</math>라 두자. | ||
| − | 이를 풀면 | + | 이를 풀면 다음의 미분방정식을 얻는다. |
| + | :<math>\frac{dx}{dy}=\sqrt{\frac{y}{2a-y}}</math> | ||
(미분방정식의 여러 해에 대한 논의는 http://whistleralley.com/brachistochrone/brachistochrone.htm) | (미분방정식의 여러 해에 대한 논의는 http://whistleralley.com/brachistochrone/brachistochrone.htm) | ||
| − | + | <math>x=\int_{0}^{y}\sqrt{\frac{y}{2a-y}}dy</math>, <math>y=2a\sin^2\frac{\theta}{2}=a(1-\cos\theta)</math>로 치환하면, <math>x=a(\theta-\sin\theta)</math>를 얻는다. | |
| − | |||
| − | <math>y=2a\sin^2\frac{\theta}{2}=a(1-\cos\theta)</math>로 치환하면, <math>x=a(\theta-\sin\theta)</math>를 얻는다. | ||
여기서 상수 a는 주어진 점 <math>(x_1,y_1)</math>를 지날 수 있는 값으로 결정된다. | 여기서 상수 a는 주어진 점 <math>(x_1,y_1)</math>를 지날 수 있는 값으로 결정된다. | ||
| 50번째 줄: | 38번째 줄: | ||
따라서 사이클로이드를 얻었다.■ | 따라서 사이클로이드를 얻었다.■ | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==재미있는 사실== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Half-pipe ? | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Half-pipe ? | ||
* Half-Pipe Skateboarding ? | * Half-Pipe Skateboarding ? | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==수학용어번역== | |
| − | + | * Brachistochrone curve | |
| + | ** brachistos - the shortest, chronos - time | ||
| + | ** 최단시간강하 곡선, 최속강하선, 최단강하선 | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==관련된 항목들== | |
| − | + | * [[오일러-라그랑지 방정식]] | |
| − | * [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| + | ==매스매티카 파일 및 계산 리소스== | ||
| + | * http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/TheGreatBrachistochroneRace/ | ||
| + | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==사전 형태의 자료== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* http://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | * http://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | ||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brachistochrone_problem | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brachistochrone_problem | ||
| − | * http:// | + | * http://curvebank.calstatela.edu/brach/brach.htm |
| − | + | * http://mathworld.wolfram.com/BrachistochroneProblem.html | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==관련논문== | |
| − | * [http://www.jstor.org/stable/4146894 The Brachistochrone Problem] | + | * [http://www.jstor.org/stable/4146894 The Brachistochrone Problem] |
** Nils P. Johnson, The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 35, No. 3 (May, 2004), pp. 192-197 | ** Nils P. Johnson, The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 35, No. 3 (May, 2004), pp. 192-197 | ||
| − | * [http://www.jstor.org/stable/2974953 Exploring the Brachistochrone Problem] | + | * [http://www.jstor.org/stable/2974953 Exploring the Brachistochrone Problem] |
** LaDawn Haws, Terry Kiser, The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 102, No. 4 (Apr., 1995), pp. 328-336 | ** LaDawn Haws, Terry Kiser, The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 102, No. 4 (Apr., 1995), pp. 328-336 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==관련도서== | |
* http://books.google.com/books?id=dptKVr-5LJAC&pg=PA223&sig=PVA7Q1U_MyXinobyhOf54BwjShQ&hl=en#v=onepage&q&f=false | * http://books.google.com/books?id=dptKVr-5LJAC&pg=PA223&sig=PVA7Q1U_MyXinobyhOf54BwjShQ&hl=en#v=onepage&q&f=false | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==링크== | |
| − | + | * [http://curvebank.calstatela.edu/brach/brach.htm The Brachistochrone] | |
| − | + | [[분류:곡선]] | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | == 노트 == | |
| − | + | ===말뭉치=== | |
| + | # More specifically, the brachistochrone can use up to a complete rotation of the cycloid (at the limit when A and B are at the same level), but always starts at a cusp.<ref name="ref_9b3bb6c7">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brachistochrone_curve Brachistochrone curve]</ref> | ||
| + | # According to Newtonian scholar Tom Whiteside, in an attempt to outdo his brother, Jakob Bernoulli created a harder version of the brachistochrone problem.<ref name="ref_9b3bb6c7" /> | ||
| + | # Johann Bernoulli's direct method is historically important as it was the first proof that the brachistochrone is the cycloid.<ref name="ref_9b3bb6c7" /> | ||
| + | # In this blog post, we demonstrate how to use built-in mathematical expressions and the Optimization Module in COMSOL Multiphysics to solve for the brachistochrone curve.<ref name="ref_264bcfed">[https://www.comsol.com/blogs/how-to-solve-for-the-brachistochrone-curve-between-points/ How to Solve for the Brachistochrone Curve Between Points]</ref> | ||
| + | # The brachistochrone curve is an idealized curve that provides the fastest descent possible.<ref name="ref_264bcfed" /> | ||
| + | # Next, we use an interpolation function to approximate the brachistochrone curve.<ref name="ref_264bcfed" /> | ||
| + | # The brachistochrone curve is a classic physics problem, that derives the fastest path between two points A and B which are at different elevations.<ref name="ref_aeddd8c4">[https://www.instructables.com/The-Brachistochrone-Curve/ The Brachistochrone Curve]</ref> | ||
| + | # There is no better way to learn than through STEM, so follow on to make your very own working brachistochrone model.<ref name="ref_aeddd8c4" /> | ||
| + | # Before I end I must voice once more the admiration I feel for the unexpected identity of Huygens' tautochrone and my brachistochrone.<ref name="ref_4722e185">[https://mathshistory.st-andrews.ac.uk/HistTopics/Brachistochrone/ Brachistochrone problem]</ref> | ||
| + | # This article presents the problem of quickest descent, or the Brachistochrone curve, that may be solved by the calculus of variations and the Euler-Lagrange equation.<ref name="ref_68ed8ad5">[https://www.tau.ac.il/~flaxer/edu/course/computerappl/exercise/Brachistochrone%20Curve.pdf Osaka keidai ronshu, vol. 61 no. 6 march 2011]</ref> | ||
| + | # The rst step in the solution of the Euler-Lagrange equation for the brachistochrone problem: is to reduce it to a rst-order equation.<ref name="ref_ef0bb1d5">[http://www.math.utk.edu/~freire/teaching/m231f08/m231f08brachistochrone.pdf The brachistochrone problem.]</ref> | ||
| + | # the red cycloid beats the other two It can also be asked what the brachistochrone curve among the curves joining two points and having a given shape would be.<ref name="ref_b32ffb35">[https://mathcurve.com/courbes2d.gb/brachistochrone/brachistochrone.shtml Brachistochrone]</ref> | ||
| + | # For example, for two points at the same altitude and V-shaped curves, the brachistochrone curve is the one for which the angle of the V is a right angle, as is shown in the animation opposite.<ref name="ref_b32ffb35" /> | ||
| + | # The problem of the brachistochrone with given length is studied on this page.<ref name="ref_b32ffb35" /> | ||
| + | # One can also try to find the brachistochrone "with friction".<ref name="ref_b32ffb35" /> | ||
| + | # The brachistochrone problem was one of the earliest problems posed in the calculus of variations.<ref name="ref_f5cca441">[https://mathworld.wolfram.com/BrachistochroneProblem.html Brachistochrone Problem -- from Wolfram MathWorld]</ref> | ||
| + | # Brachistochrone, the planar curve on which a body subjected only to the force of gravity will slide (without friction) between two points in the least possible time.<ref name="ref_5bcf547e">[https://www.britannica.com/science/brachistochrone Brachistochrone | physics]</ref> | ||
| + | # The name brachistochrone comes from two Greek words, brachistos meaning shortest, and chronos meaning time.<ref name="ref_02e66dfd">[https://www.myphysicslab.com/roller/brachistochrone-en.html myPhysicsLab Brachistochrone]</ref> | ||
| + | # The brachistochrone curve can be generated by tracking a point on the rim of a wheel as it rolls on the ground.<ref name="ref_02e66dfd" /> | ||
| + | # This mathematical challenge is known as the problem of the brachistochrone.<ref name="ref_e19ac3b2">[https://medium.com/cantors-paradise/the-famous-problem-of-the-brachistochrone-8b955d24bdf7 The Famous Problem of the Brachistochrone]</ref> | ||
| + | # Figure 3: Newton’s handwritten solution to the brachistochrone problem (source).<ref name="ref_e19ac3b2" /> | ||
| + | # The classical problem in calculus of variation is the so called brachistochrone problem 1 posed (and solved) by Bernoulli in 1696.<ref name="ref_69295678">[https://wiki.math.ntnu.no/_media/tma4180/2015v/calcvar.pdf Basics of calculus of variations]</ref> | ||
| + | # Abstract: This article presents the problem of quickest descent, or the Brachistochrone curve, that may be solved by the calculus of variations and the Euler-Lagrange equation.<ref name="ref_b10a7db6">[https://ijpam.eu/contents/2013-82-3/8/8.pdf International journal of pure and applied mathematics]</ref> | ||
| + | # Historically and pedagogically, the prototype problem introducing the cal- culus of variations is the brachistochrone, from the Greek for shortest time.<ref name="ref_15b1f6a4">[http://www.hep.caltech.edu/~fcp/math/variationalCalculus/variationalCalculus.pdf Physics 129a]</ref> | ||
| + | ===소스=== | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
| − | + | == 메타데이터 == | |
| − | + | ===위키데이터=== | |
| − | + | * ID : [https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q529985 Q529985] | |
| − | + | ===Spacy 패턴 목록=== | |
| − | * | + | * [{'LOWER': 'brachistochrone'}, {'LEMMA': 'curve'}] |
| − | + | * [{'LEMMA': 'brachistochrone'}] | |
| − | * [ | ||
| − | * [ | ||
2021년 2월 23일 (화) 18:09 기준 최신판
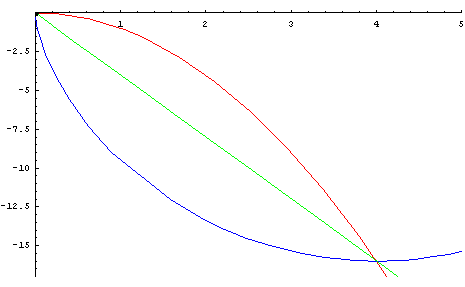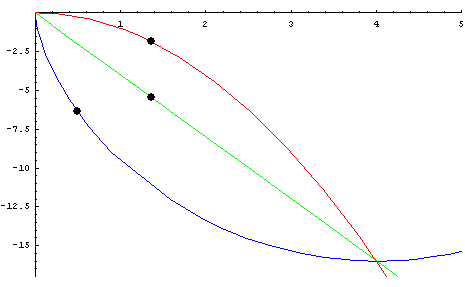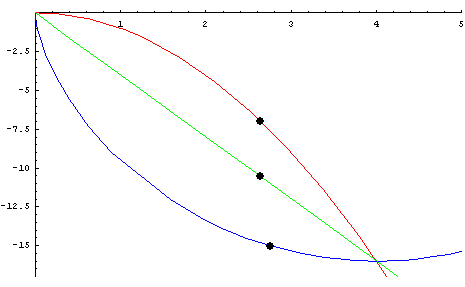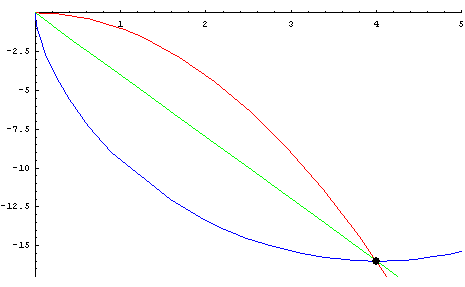
개요
- 중력을 받고 있는 물체가 정지상태에서 출발하여 가장 짧은 시간내에 하강하기 위해서 따라야 하는 곡선
- 1697년에 베르누이에 의하여 답이 출판
곡선의 시작점을 \((x_0,y_0)=(0,0)\), 끝점을 \((x_1,y_1)\)라 두자.
곡선을 따라 내려올때 걸리는 시간은 다음과 같이 구할 수 있다.
\(t=\int \frac{1}{v} \, ds\)(v는 속력, ds 는 길이요소, t는 시간)
에너지 보존 법칙 \(mgy=\frac{1}{2}mv^2\) 에서\(v=\sqrt{2gy}\).
이제 곡선의 x좌표를 y의 함수로 생각하자. 곡선을 따라 내려올 때 걸리는 시간은 \[T=\int \frac{1}{v} \, ds=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2g}}\int_{0}^{y} \frac{\sqrt{1+x'(y)^2}}{\sqrt{y}} \, dy\]
문제의 정의에 따라 이 적분값을 최소가 되게 하는 곡선을 찾아야 한다.
\(F(y,x,x')=\frac{\sqrt{1+(x')^2}}{\sqrt{y}}\) 에 대하여 오일러-라그랑지 방정식 을 적용하면, \[0 =\frac{\partial F}{\partial x} - \frac{d}{dy} \frac{\partial F}{\partial x'}=-\frac{d}{dy}(\frac{x'(y)}{\sqrt{y(1+x'(y)^2)}})\]
적당한 상수 a에 대하여 \(\frac{x'(y)}{\sqrt{y(1+x'(y)^2)}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2a}}\)라 두자.
이를 풀면 다음의 미분방정식을 얻는다. \[\frac{dx}{dy}=\sqrt{\frac{y}{2a-y}}\]
(미분방정식의 여러 해에 대한 논의는 http://whistleralley.com/brachistochrone/brachistochrone.htm)
\(x=\int_{0}^{y}\sqrt{\frac{y}{2a-y}}dy\), \(y=2a\sin^2\frac{\theta}{2}=a(1-\cos\theta)\)로 치환하면, \(x=a(\theta-\sin\theta)\)를 얻는다.
여기서 상수 a는 주어진 점 \((x_1,y_1)\)를 지날 수 있는 값으로 결정된다.
따라서 사이클로이드를 얻었다.■
재미있는 사실
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Half-pipe ?
- Half-Pipe Skateboarding ?
수학용어번역
- Brachistochrone curve
- brachistos - the shortest, chronos - time
- 최단시간강하 곡선, 최속강하선, 최단강하선
관련된 항목들
매스매티카 파일 및 계산 리소스
사전 형태의 자료
- http://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brachistochrone_problem
- http://curvebank.calstatela.edu/brach/brach.htm
- http://mathworld.wolfram.com/BrachistochroneProblem.html
관련논문
- The Brachistochrone Problem
- Nils P. Johnson, The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 35, No. 3 (May, 2004), pp. 192-197
- Exploring the Brachistochrone Problem
- LaDawn Haws, Terry Kiser, The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 102, No. 4 (Apr., 1995), pp. 328-336
관련도서
링크
노트
말뭉치
- More specifically, the brachistochrone can use up to a complete rotation of the cycloid (at the limit when A and B are at the same level), but always starts at a cusp.[1]
- According to Newtonian scholar Tom Whiteside, in an attempt to outdo his brother, Jakob Bernoulli created a harder version of the brachistochrone problem.[1]
- Johann Bernoulli's direct method is historically important as it was the first proof that the brachistochrone is the cycloid.[1]
- In this blog post, we demonstrate how to use built-in mathematical expressions and the Optimization Module in COMSOL Multiphysics to solve for the brachistochrone curve.[2]
- The brachistochrone curve is an idealized curve that provides the fastest descent possible.[2]
- Next, we use an interpolation function to approximate the brachistochrone curve.[2]
- The brachistochrone curve is a classic physics problem, that derives the fastest path between two points A and B which are at different elevations.[3]
- There is no better way to learn than through STEM, so follow on to make your very own working brachistochrone model.[3]
- Before I end I must voice once more the admiration I feel for the unexpected identity of Huygens' tautochrone and my brachistochrone.[4]
- This article presents the problem of quickest descent, or the Brachistochrone curve, that may be solved by the calculus of variations and the Euler-Lagrange equation.[5]
- The rst step in the solution of the Euler-Lagrange equation for the brachistochrone problem: is to reduce it to a rst-order equation.[6]
- the red cycloid beats the other two It can also be asked what the brachistochrone curve among the curves joining two points and having a given shape would be.[7]
- For example, for two points at the same altitude and V-shaped curves, the brachistochrone curve is the one for which the angle of the V is a right angle, as is shown in the animation opposite.[7]
- The problem of the brachistochrone with given length is studied on this page.[7]
- One can also try to find the brachistochrone "with friction".[7]
- The brachistochrone problem was one of the earliest problems posed in the calculus of variations.[8]
- Brachistochrone, the planar curve on which a body subjected only to the force of gravity will slide (without friction) between two points in the least possible time.[9]
- The name brachistochrone comes from two Greek words, brachistos meaning shortest, and chronos meaning time.[10]
- The brachistochrone curve can be generated by tracking a point on the rim of a wheel as it rolls on the ground.[10]
- This mathematical challenge is known as the problem of the brachistochrone.[11]
- Figure 3: Newton’s handwritten solution to the brachistochrone problem (source).[11]
- The classical problem in calculus of variation is the so called brachistochrone problem 1 posed (and solved) by Bernoulli in 1696.[12]
- Abstract: This article presents the problem of quickest descent, or the Brachistochrone curve, that may be solved by the calculus of variations and the Euler-Lagrange equation.[13]
- Historically and pedagogically, the prototype problem introducing the cal- culus of variations is the brachistochrone, from the Greek for shortest time.[14]
소스
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Brachistochrone curve
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 How to Solve for the Brachistochrone Curve Between Points
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 The Brachistochrone Curve
- ↑ Brachistochrone problem
- ↑ Osaka keidai ronshu, vol. 61 no. 6 march 2011
- ↑ The brachistochrone problem.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Brachistochrone
- ↑ Brachistochrone Problem -- from Wolfram MathWorld
- ↑ Brachistochrone | physics
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 myPhysicsLab Brachistochrone
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 The Famous Problem of the Brachistochrone
- ↑ Basics of calculus of variations
- ↑ International journal of pure and applied mathematics
- ↑ Physics 129a
메타데이터
위키데이터
- ID : Q529985
Spacy 패턴 목록
- [{'LOWER': 'brachistochrone'}, {'LEMMA': 'curve'}]
- [{'LEMMA': 'brachistochrone'}]