"Lectures on dilogarithm function"의 두 판 사이의 차이
imported>Pythagoras0 |
imported>Pythagoras0 |
||
| 1번째 줄: | 1번째 줄: | ||
==overview== | ==overview== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* definition of dilogarithm function | * definition of dilogarithm function | ||
* analytic continuation | * analytic continuation | ||
| + | * functional equations | ||
* Bloch-Wigner dilogarithm function | * Bloch-Wigner dilogarithm function | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* values of the Dedekind zeta function at s=2 | * values of the Dedekind zeta function at s=2 | ||
| + | * volumes of hyperbolic 3-manifolds | ||
| − | + | ==introdcution== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
* 다이로그 함수는 복소수 <math>|z|<1</math>에 대하여 다음과 같이 정의됨:<math>\operatorname{Li}_ 2(z)= \sum_{n=1}^\infty {z^n \over n^2}</math>:<math>|z|\leq 1</math> 에서 고르게 수렴하는 급수이므로, <math>|z|\leq 1</math>에서 연속 | * 다이로그 함수는 복소수 <math>|z|<1</math>에 대하여 다음과 같이 정의됨:<math>\operatorname{Li}_ 2(z)= \sum_{n=1}^\infty {z^n \over n^2}</math>:<math>|z|\leq 1</math> 에서 고르게 수렴하는 급수이므로, <math>|z|\leq 1</math>에서 연속 | ||
* 다음과 같은 적분으로 정의하면 해석적으로 확장가능:<math>\operatorname{Li}_ 2(z) = -\int_0^z{{\ln (1-t)}\over t} dt </math> for <math>z\in \mathbb C-[1,\infty)</math> | * 다음과 같은 적분으로 정의하면 해석적으로 확장가능:<math>\operatorname{Li}_ 2(z) = -\int_0^z{{\ln (1-t)}\over t} dt </math> for <math>z\in \mathbb C-[1,\infty)</math> | ||
2018년 3월 23일 (금) 19:01 판
overview
- definition of dilogarithm function
- analytic continuation
- functional equations
- Bloch-Wigner dilogarithm function
- values of the Dedekind zeta function at s=2
- volumes of hyperbolic 3-manifolds
introdcution
- 다이로그 함수는 복소수 \(|z|<1\)에 대하여 다음과 같이 정의됨\[\operatorname{Li}_ 2(z)= \sum_{n=1}^\infty {z^n \over n^2}\]\[|z|\leq 1\] 에서 고르게 수렴하는 급수이므로, \(|z|\leq 1\)에서 연속
- 다음과 같은 적분으로 정의하면 해석적으로 확장가능\[\operatorname{Li}_ 2(z) = -\int_0^z{{\ln (1-t)}\over t} dt \] for \(z\in \mathbb C-[1,\infty)\)
special values
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(0)=0\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(1)=\frac{\pi^2}{6}\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(-1)=-\frac{\pi^2}{12}\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{1}{2})=\frac{\pi^2}{12}-\frac{1}{2}\log^2(2)\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2})=\frac{\pi^2}{15}-\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2})=\frac{\pi^2}{10}-\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{1-\sqrt{5}}{2})=-\frac{\pi^2}{15}+\frac{1}{2}\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{-1-\sqrt{5}}{2})=-\frac{\pi^2}{10}+\frac{1}{2}\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})\)
functional equations
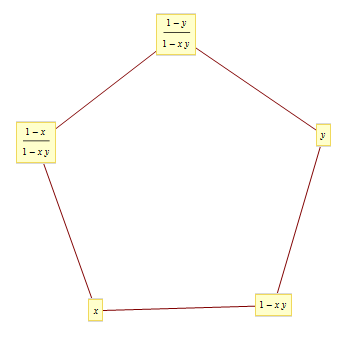
- 5항 관계식은 다이로그 함수의 가장 중요한 항등식의 하나이다.\[\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2(y)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{1-x}{1-xy} \right)+\mbox{Li}_ 2(1-xy)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{1-y}{1-xy} \right)=\frac{\pi^2}{2}-\log(x)\log(1-x)-\log(y)\log(1-y)+\log (\frac{1-x}{1-xy})\log (\frac{1-y}{1-xy})\]
5항 관계식
- 로저스 다이로그 함수 \(L(x)\)
- \(0\leq x,y\leq 1\) 일 때, 다음이 성립한다
\[L(x)+L(1-xy)+L(y)+L\left(\frac{1-y}{1-xy}\right)+L\left(\frac{1-x}{1-xy} \right)=\frac{\pi^2}{2}\]
- \(1-x_{i}=x_{i-1}x_{i+1}\), \(x_0=x\), \(x_2=y\)로 정의되는 점화식은 주기가 5인 수열이 된다\[x_0=x, x_1=1-xy, x_2=y, x_3=\frac{1-y}{1-xy}, x_4=\frac{1-x}{1-xy}\]
- 집합 \(\{0,1,\infty,y,xy\}\) 에서 4개의 원소를 뽑아 얻어지는 교차비(cross ratio)
Rogers dilogarithm
- \(x\in (0,1)\)에서 로저스 다이로그 함수를 다음과 같이 정의
\[L(x)=\operatorname{Li}_ 2(x)+\frac{1}{2}\log x\log (1-x)=-\frac{1}{2}\int_{0}^{x}\left(\frac{\log(1-y)}{y}+\frac{\log(y)}{1-y}\right)dy\]
- \((-\infty,0],[1,+\infty)\)를 제외한 복소평면으로 해석적확장됨
- \(dL(y)=\frac{1}{2}[\log(y)d\log (1-y)-\log(1-y)d\log (y)]\)
algebraic K-theory
- $F$ : number field
- $K_0(F) = \mathbb{Z}$
- $K_1(F) = F^{\times}$
- $K_2(F) = F^{\times}\otimes F^{\times}/\langle x\otimes (1-x) \rangle$
- $K_0(\mathcal{O}_F) = \mathbb{Z}\oplus Cl_F$
- $K_1(\mathcal{O}_F) = (\mathcal{O}_F)^{\times}$
- $K_2(\mathcal{O}_F)$ : finite group
Borel's regulator
- Let $F$ be a number field with $[F:\mathbb{Q}]=r_1+2r_2$
- Borel constructed a map
$$ K_{2i-1}(F) \to \mathbb{R}^{d_{i}} $$ where $d_i = r_2$ or $r_1+r_2$ depending on the parity of $i$
- this can be used to show
- $\operatorname{rank} K_3 =r_2$
- $\operatorname{rank} K_5=r_1+r_2$
- $\operatorname{rank} K_7=r_2$
- let $\mathcal{O}_{F}$ be the ring of integers of $F$
- for any field L of characteristic zero, $K_{i}(\mathcal{O}_{F})\otimes_{\Z}L$ is naturally isomorphic to $K_{i}(F)\otimes_{\Z}L$ for $i>1$
- http://www.ams.org/mathscinet-getitem?mr=1354171
- https://books.google.nl/books?id=ru7BywKC1d4C&pg=PA475&lpg=PA475&dq=Values+of+zeta-functions+at+integers,+cohomology+and+polylogarithms&source=bl&ots=BznObLSgR-&sig=X9LeM98z4cxje_axpCZjeUaY66U&hl=en&sa=X&ei=5rCMU-bqNMLwPInpgLgH&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Values%20of%20zeta-functions%20at%20integers%2C%20cohomology%20and%20polylogarithms&f=false
Bloch-Wigner dilogarithm
- Let us define a variant of the dilogarithm function : the Bloch-Wigner dilogarithm function. It is given by
$$D(z)=\text{Im}(\operatorname{Li}_2(z))+\log|z|\arg(1-z).$$
- It is a real analytic function on $\mathbb{C}$ except at 0 and 1, where it is continuous but not differentiable.
- Since $D(\bar{z})=-D(z)$, it vanishes on $\mathbb{R}$.
- It satisfies the following functional equations :
\begin{equation}\label{functid1} D(x)+D(1-xy)+D(y)+D(\frac{1-y}{1-xy})+D(\frac{1-x}{1-xy})=0, \end{equation} \begin{equation}\label{functid2} D(x)+D(1-x) =D(x)+D(\frac{1}{x})=0. \end{equation}
regulator in algebraic K-theory
- The Bloch-Wigner dilogarithm $D(z)$ can be used to define a map from $\mathcal{B}(\mathbb{C})$ to $\mathbb{R}$.
- For $\xi=\sum_{i} n_i[x_i] \in \mathcal{B}(\mathbb{C})$, let $D(\xi)=\sum_{i} n_i D(x_i)$.
- By (\ref{functid1}) and (\ref{functid2}), it is well-defined.
- Let $F$ be a number field of degree $r_1+2r_2$ over $\mathbb{Q}$ where $r_1$ denotes the number of real embeddings and $r_2$ the number of complex non-real embeddings up to conjugation.
- For an embedding $\sigma : F\hookrightarrow \mathbb{C}$ and $\xi \in \mathcal{B}(F)$, we may consider $D\left(\sigma(\xi)\right)$.
- If $D\left(\sigma(\xi)\right)=0$ for all such embeddings $\sigma$, then $\xi \in \mathcal{B}(F)$ is a torsion element in $\mathcal{B}(F)$.
Dedekind zeta
- 데데킨트 제타함수에 대해서 다음과 같은 함수방정식이 성립
\[\xi_{K}(s)=\left|d_K\right|{}^{s/2} 2^{r_2 (1-s)} \pi ^{\frac{1}{2} \left(-r_1-2 r_2\right) s}\Gamma \left(\frac{s}{2}\right)^{r_1} \Gamma (s)^{r_2}\zeta _K(s)\]\[\xi_{K}(s) = \xi_{K}(1 - s)\]
- at $s=-n, n=1,2\cdots$, $\zeta_K(s)$ has zero of order $r_2$ or $r_1+r_2$ if $n$ is even or odd, respectively
$$ 2^{(m+1) r_2} \pi^{-\frac{1}{2} m \left(-r_1-2 r_2\right)}\zeta_K(-m) \Gamma (-m)^{r_2}\Gamma(-\frac{m}{2} )^{r_1} \left| d_K\right| {}^{-\frac{m}{2}}\\ =2^{-m r_2} \pi ^{\frac{1}{2} (m+1) \left(-r_1-2 r_2\right)} \zeta _K(m+1)\Gamma(\frac{m+1}{2})^{r_1}\Gamma (m+1)^{r_2} \left| d_K\right| {}^{\frac{m+1}{2}} $$
- this implies
$$ \pi^{-d_m} \lim_{s\to -m}\frac{\zeta_K(-m)}{(s+m)^{d_m}} \sim_{\mathbb{Q}^{\times}}\pi ^{-(m+1)(r_1+2 r_2)} \zeta _K(m+1)\left| d_K\right| {}^{\frac{1}{2}} $$ where $d_1 =d_3=\dots = r_2$ or $d_2=d_4=\dots =r_1+r_2$
디리클레 유수 공식
- \(s=1\) 에서의 유수(residue)는 디리클레 유수 (class number) 공식으로 주어진다
\[ \lim_{s\to 1} (s-1)\zeta_K(s)=\frac{2^{r_1}\cdot(2\pi)^{r_2}\cdot h_K\cdot R_K}{w_K \cdot \sqrt{|d_K|}}\]
- \(s=0\) 에서 order 가 \(r_1+r_2-1\) 인 zero를 가지며 다음이 성립한다\[ \lim_{s\to 0}\frac{\zeta_K(s)}{s^{r_1+r_2-1}}=-\frac{h_K R_K}{w_K}\]
Zagier, Bloch, Suslin
- \([K : \mathbb{Q}] = r_1 + 2r_2\)일 때,
\[ \frac{|d_{K}|^{1/2}}{\pi^{2(r_1 + r_2)}} \zeta_{K}(2) \sim_{\mathbb{Q^{\times}}} \det\left(D(\sigma_i(\xi_j))\right)_{1\leq i,j\leq r_2} \] 여기서 \(\xi_i,(i=1,\cdots, r_2)\) 는 Bloch group \(B(K)\otimes \mathbb{Q}\)의 $\mathbb{Q}$-basis D는 블로흐-비그너 다이로그(Bloch-Wigner dilogarithm) 함수이며, \(a\sim_{\mathbb{Q^{\times}}} b\) 는 \(a/b\in\mathbb{Q}\) 를 의미함
background
- 다른게 아니라 저랑 강원대 강순이 박사님이랑 최근에 Zagier 교수님 쓰신 dilogarithm 논문에 관심이 생겼는데 quantum dilogarithm을 포함해서 자기에 교수님 논문 내용을 강연해줄 수 있는지 부탁드리고자 편지드려요.
- Bloc 그룹도 강의해줄 수 있으면 더 좋지만, 아니면 남 추측 관련해서 공부했던 내용이라도 강의해주면 많은 도움이 될 것 같아요.
- 자기에 교수님 dilogarithm 논문을 읽는데, 부끄럽지만 무슨 말인지 전혀 모르겠더라고요.
- q가 나오는 부분과 점근식 부분은 그래도 알겠는데, 나머지 부분들은 능력 밖이라 도움 받을 수 있나해서 여쭤본 겁니다.
- 그러니까 Bloc 그룹도 이 논문에 나오는 정도 이해할 수 있으면 저는 만족이에요.
- quantum dilogarithm 쪽으로 무언가 더 해볼 여지가 있는지 궁금해서 우선 자기에 교수님 논문부터 시작해보려고 했었는데, 시작부터 어렵네요