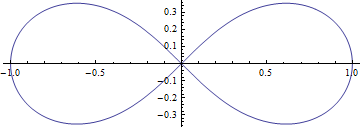
렘니스케이트(lemniscate) 곡선의 길이와 타원적분
개요
- 극좌표계에서 방정식 \(r^2=\cos2\theta\) 로 주어진 곡선을 베르누이의 렘니스케이트 곡선이라 부름.
- 카테시안 좌표계에서는 \((x^2 + y^2)^2=x^2 - y^2\)로 주어진다
렘니스케이트 곡선의 둘레의 길이와 타원적분
- 렘니스케이트 곡선의 둘레의 길이 \(L\)은 타원적분 으로 표현되며 다음과 같은 과정을 통해 얻어짐
- 곡선은 \(x=r(\theta)\cos\theta,y=r(\theta)\sin\theta\)로 매개화된다
- 매개화를 이용하여, 둘레의 길이를 계산
\[r'(\theta)=-\frac{\sin 2\theta}{r(\theta)}\] \[L=4\int_{0}^{\pi/4}\sqrt{r'(\theta)^2+r(\theta)^2}\,d\theta=4\int_{0}^{\pi/4}\sqrt{\frac{\sin^2 2\theta}{r^2(\theta)}+r^2(\theta)}\,d\theta=4\int_{0}^{\pi/4}\frac{1}{\sqrt{\cos 2\theta}}\,d\theta\]
- 이 때, \(\cos 2\theta=\cos^2{\phi}\) 를 이용하여 치환하면,
\[d\theta=\frac{\sin\phi\cos\phi}{\sqrt{1-\cos^4\phi}}\,d\phi=\frac{\cos\phi}{\sqrt{1+\cos^2\phi}}\,d\phi\] \[L=4\int_0^{\pi/2}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\cos^2 \phi}}\,d\phi=2\sqrt{2}\int_0^{\pi/2}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{1}{2}\sin^2 \phi}}\,d\phi=2\sqrt{2}K(1/\sqrt{2})\]
- \(x=\cos\phi\) 로 치환하면,
\[L=4\int_0^{\pi/2}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\cos^2 \phi}}\,d\phi=4\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^4}}=\frac{\Gamma(1/4)^2}{\sqrt{2\pi}}=5.2441\cdots\]
가우스의 렘니스케이트 상수
- \(\omega:=L/2=2.62\cdots\) 를 가우스의 렘니스케이트 상수라 함\[L=2\omega=4\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^4}}=B(1/2,1/4)=\frac{\Gamma(\frac{1}{2})\Gamma(\frac{1}{4})}{\Gamma(\frac{3}{4})}=\frac{\Gamma(1/4)^2}{\sqrt{2\pi}}=5.24\cdots\]
- 타원곡선 y²=x³-x의 주기(periods)이며 초월수 임.
원주율과의 비교
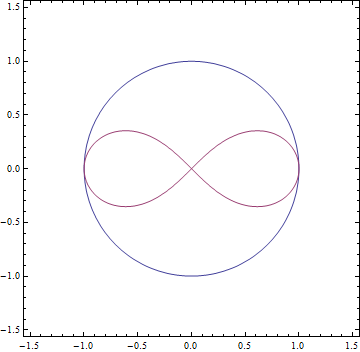
- 가우스가 계산한 값은 원의 둘레의 길이와 렘니스케이트의 둘레의 길이의 비율\[\frac{\pi}{2}=\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}=1.57\cdots\]\[\frac{\omega}{2}=\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^4}}=1.31\cdots\]\[\frac{\pi }{\omega}=1.1981402347\cdots\] 가 얻어짐
- 한편\(AGM(a,b)\) 은 두 수 a, b의 산술기하평균을 말하는 것으로 다음과 같은 점화식의 극한으로 정의됨.
\[a_0=a, b_0=b,a_{n+1}=\frac{a_n+b_n}{2},b_{n+1}=\sqrt{a_nb_n}\]
- 가우스의 계산으로는 \(AGM(1,\sqrt2)\)과 같음
- 단위원과 렘니스케이트 곡선
가우스의 계산 타원적분을 통한 증명
- 렘니스케이트 상수의 타원적분 표현
$$\frac{\omega}{2}=\int_0^1\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x^4}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \frac{d\theta}{\sqrt{1-\frac{1}{2}\sin^2\theta}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}K(\frac{1}{\sqrt2})\label{ome}$$
- 랜든변환(Landen's transformation) 에서 얻어진 결과에서 $$K(\frac{1}{\sqrt2})=\frac{\pi}{2M(1,\frac{1}{\sqrt2})}\label{landen}$$
- \ref{ome}와 \ref{landen}를 이용하여 다음을 얻는다:
$$\frac{\pi}{\omega}=\frac{2K(\frac{1}{\sqrt2}){M(1,\frac{1}{\sqrt2})}}{\sqrt{2}K(\frac{1}{\sqrt2})} = \sqrt{2}M(1,\frac{1}{\sqrt2})=M(1,\sqrt2)$$ 여기서 $$K(k) = \int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \frac{d\theta}{\sqrt{1-k^2 \sin^2\theta}}.$$
재미있는 사실
- 곡선의 모양이 무한대 기호와 같음
- 무한대는 그 한계가 없기에 리본을 뜻하는 'lemniscus'라는 말로 불릴 때도 있었으며, 그로인해 무한대 기호가 누운 8자 모양이 되었다는 설이 있음
역사
- 1684 베르누이 'Acta Eruditorum'
- 18세기 Fagnano, Euler, and Legendre 에 의한 연구
- 1798~1799년의 시기에 가우스는 이 곡선의 길이와 관련하여 다음과 같은 기록을 일기에 남김. (Pi-unleashed, 99p)
We have gained some very elegant details about the lemniscate, which have exceeded all expectations, and indeed using methods which open up an entirely new field. That the AGM is equal to \(\frac{\pi }{\omega}\) between 1 and \(\sqrt{2}\) we have confirmed up to the 11th decimal digit; if this is proven, then a truly new field of analysis stands before us.
- 수학사 연표
- Gauss' study of lemniscate curve and elliptic integrals
관련된 항목들
수학용어번역
- http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en|ko&q=lemniscate
- Latin lemniscus meaning "ribbon"
- 번역용어제안
- 쌍타원, 겹타원, 이중타원, 나비리본
- '베르누이의 연주형'(lemniscate) http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=ko|ko&q=연주
- lemniscate - 대한수학회 수학용어집
매스매티카 파일 및 계산 리소스
- https://docs.google.com/leaf?id=0B8XXo8Tve1cxZjRmZjkwMjgtNGY0Mi00MzllLWExMGQtZjExZjIzZWMyNDRk&sort=name&layout=list&num=50
- http://mathworld.wolfram.com/LemniscateConstant.html
- The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences
- http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=Lemniscate
- http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=integrate_0^{1}+1/sqrt(1-x^4)+dx
- http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=integrate_1^{infty}+1/sqrt(x^3-x)+dx
- http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=Beta(1/2,1/4)
사전 형태의 자료
- http://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/렘니스케이트
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/lemniscate
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infinity
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gauss's_constant
관련도서
- Mathematics by experiment: plausible reasoning in the 21st century
- M. Borwein and D. H. Bailey, , A K Peters, Natick, MA, 2003.
관련논문과 에세이
- From Lintearia to Lemniscate I : physics to mathematics R Sridharan
- From Lintearia to Lemniscate II: Gauss and Landen’s Work R Sridharan
- The Lemniscate and Fagnano's Contributions to Elliptic IntegralsRaymond Ayoub, Archive for History of Exact Sciences, 1984