"이차곡선과 회전변환"의 두 판 사이의 차이
둘러보기로 가기
검색하러 가기
Pythagoras0 (토론 | 기여) |
Pythagoras0 (토론 | 기여) |
||
| 32번째 줄: | 32번째 줄: | ||
* [[포락선(envelope)과 curve stitching]] 에서 얻어진 곡선 <math>x^2-2 x y-20 x+y^2-20 y+100=0</math>가 포물선임을 보이려 한다 | * [[포락선(envelope)과 curve stitching]] 에서 얻어진 곡선 <math>x^2-2 x y-20 x+y^2-20 y+100=0</math>가 포물선임을 보이려 한다 | ||
| + | [[파일:9431928-parabola2.gif]] | ||
* <math>a=c=1</math> 이므로, <math>\theta</math>에 대한 다음 방정식을 얻는다:<math>\cot (2 \theta )=\frac{a-c}{b}=0</math><br> | * <math>a=c=1</math> 이므로, <math>\theta</math>에 대한 다음 방정식을 얻는다:<math>\cot (2 \theta )=\frac{a-c}{b}=0</math><br> | ||
* <math>\theta=\pi/4</math> 는 이 방정식의 해이므로, <math>x\to X \cos (\theta )-Y \sin (\theta ),y\to X \sin (\theta )+Y \cos (\theta )</math> 즉:<math>x\to \frac{X}{\sqrt{2}}-\frac{Y}{\sqrt{2}},y\to \frac{X}{\sqrt{2}}+\frac{Y}{\sqrt{2}}</math> 를 이용할 수 있다<br> | * <math>\theta=\pi/4</math> 는 이 방정식의 해이므로, <math>x\to X \cos (\theta )-Y \sin (\theta ),y\to X \sin (\theta )+Y \cos (\theta )</math> 즉:<math>x\to \frac{X}{\sqrt{2}}-\frac{Y}{\sqrt{2}},y\to \frac{X}{\sqrt{2}}+\frac{Y}{\sqrt{2}}</math> 를 이용할 수 있다<br> | ||
| 69번째 줄: | 70번째 줄: | ||
* https://docs.google.com/file/d/0B8XXo8Tve1cxZDUzMTM1NDItNGUzNC00NTk5LTk1OTYtMGUzMThiODAzN2Q3/edit | * https://docs.google.com/file/d/0B8XXo8Tve1cxZDUzMTM1NDItNGUzNC00NTk5LTk1OTYtMGUzMThiODAzN2Q3/edit | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
2013년 4월 16일 (화) 09:19 판
개요
- 일반적인 형태의 이차곡선 \(ax^2+bxy+cy^2+dx+ey+f=0,(b\neq 0)\) 이 주어진 경우, 회전변환을 이용하여 \(xy\) 항을 없앨 수 있다
- 대칭행렬의 대각화 로 이해할 수 있다
이차형식과 회전변환
이차형식 \(a x^2+b x y+c y^2\)에 \(x\to X \cos (\theta )-Y \sin (\theta ),y\to X \sin (\theta )+Y \cos (\theta )\) 를 대입하면,
이차형식 \(A X^2+B X Y+C Y^2\) 를 얻으며, 이 때의 계수는
\(A=\frac{1}{2} (a \cos (2 \theta )+a+b \sin (2 \theta )-c \cos (2 \theta )+c)\)
\(B=-a \sin (2 \theta )+b \cos (2 \theta )+c \sin (2 \theta )\)
\(C=\frac{1}{2} (a (-\cos (2 \theta ))+a-b \sin (2 \theta )+c \cos (2 \theta )+c)\)
이다.
\(\cot (2 \theta )=\frac{a-c}{b}\) 이 되도록 하는 \(\theta\)를 찾으면, \(B=0\)이 된다. (\(b=0\) 인 경우는 물론 이러한 작업이 필요하지 않다)
예
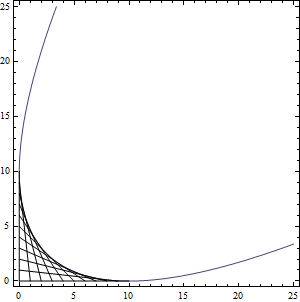
- 포락선(envelope)과 curve stitching 에서 얻어진 곡선 \(x^2-2 x y-20 x+y^2-20 y+100=0\)가 포물선임을 보이려 한다
- \(a=c=1\) 이므로, \(\theta\)에 대한 다음 방정식을 얻는다\[\cot (2 \theta )=\frac{a-c}{b}=0\]
- \(\theta=\pi/4\) 는 이 방정식의 해이므로, \(x\to X \cos (\theta )-Y \sin (\theta ),y\to X \sin (\theta )+Y \cos (\theta )\) 즉\[x\to \frac{X}{\sqrt{2}}-\frac{Y}{\sqrt{2}},y\to \frac{X}{\sqrt{2}}+\frac{Y}{\sqrt{2}}\] 를 이용할 수 있다
- \(10 \sqrt{2} X=Y^2+50\) 를 얻는다
역사
메모
- Math Overflow http://mathoverflow.net/search?q=
관련된 항목들