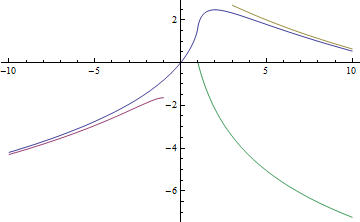"다이로그 함수(dilogarithm)"의 두 판 사이의 차이
Pythagoras0 (토론 | 기여) |
|||
| (사용자 2명의 중간 판 40개는 보이지 않습니다) | |||
| 1번째 줄: | 1번째 줄: | ||
| − | + | ==개요== | |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[폴리로그 함수(polylogarithm)|폴리로그 함수(poylogarithm)]]의 하나인 special 함수이다. |
| + | * 오일러, 로바체프스키, 아벨 등에 의하여 연구되었다. | ||
| + | * 정수론, 대수적 K-이론, 3차원 쌍곡다양체, 등각장론 등 현대수학의 많은 분야에서 중요한 역할을 한다. | ||
| + | * [[Pochhammer 기호와 캐츠(Kac) 기호|Pochhammer 기호]] <math>(q)_{n} =(q;q)_{n}=(1-q)(1-q^2)\cdots(1-q^n)</math> 의 근사식을 구하는 과정에서 자연스럽게 등장한다. | ||
| + | * 모든 [[다이로그 항등식 (dilogarithm identities)]]을 5항 관계식을 통하여 이해할 수 있는지의 여부는 다이로그 함수에 대한 중요한 미해결 문제이다 | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==정의== | |
| − | * | + | * 다이로그 함수는 복소수 <math>|z|<1</math>에 대하여 다음과 같이 정의됨:<math>\operatorname{Li}_ 2(z)= \sum_{n=1}^\infty {z^n \over n^2}</math>:<math>|z|\leq 1</math> 에서 고르게 수렴하는 급수이므로, <math>|z|\leq 1</math>에서 연속 |
| − | + | * 다음과 같은 적분으로 정의하면 해석적으로 확장가능:<math>\operatorname{Li}_ 2(z) = -\int_0^z{{\ln (1-t)}\over t} dt </math> for <math>z\in \mathbb C-[1,\infty)</math> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==함수의 그래프== | |
| + | [[파일:다이로그 함수(dilogarithm)1.gif]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==단위원에서의 실수부와 허수부== | |
| − | + | * <math>z=e^{i\theta}</math>, <math>0 \leq \theta \leq 2\pi</math> 일 때,:<math>\operatorname{Li}_ 2(e^{i\theta})= \sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{e^{in\theta}}{n^2}=\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\cos n\theta}{n^2}+i\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\sin n\theta}{n^2}</math>:<math>\mathfrak{R}(\operatorname{Li}_ 2(e^{i\theta}))=\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\cos n\theta}{n^2}=\frac{\pi^2}{6}-\frac{\theta(2\pi-\theta)}{4}</math>:<math>\mathfrak{I}(\operatorname{Li}_ 2(e^{i\theta}))=\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\sin n\theta}{n^2}=Cl_ 2(\theta)</math> | |
| + | * [[로바체프스키 함수|로바체프스키와 클라우센 함수]] 항목 참조 | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==여러가지 항등식== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* 오일러의 반사공식 | * 오일러의 반사공식 | ||
| − | <math>\mbox{Li} | + | <math>\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(x \right)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(1-x \right)= \frac{\pi^2}{6}-\ln(x)\ln(1-x)</math>, <math>0<x<1</math> |
| − | * 반전공식 | + | * 반전공식:<math>\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{1}{x} \right) = -\frac{\pi^2}{6}-\frac{1}{2}\log^2(-x)</math> |
* 란덴의 항등식 | * 란덴의 항등식 | ||
| − | <math>\mbox{Li} | + | <math>\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{-x}{1-x} \right)=-\frac{1}{2}\log^2(1-x)</math> 또는 |
| − | <math>\mbox{Li} | + | <math>\mbox{Li}_ 2(1-x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(1- \frac{1}{x} \right)=-\frac{1}{2}\log^2(x)</math> |
| − | * 여기에서 다음의 함수들은 초등함수 부분을 무시하면 같다는 것을 알 수 있음 | + | * 여기에서 다음의 함수들은 초등함수 부분을 무시하면 같다는 것을 알 수 있음:<math>\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)</math>,<math>\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(\frac{1}{1-x}\right)</math>, <math>\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(1- \frac{1}{x} \right)</math>, <math>-\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{1}{x} \right)</math>,<math>-\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(1-x \right)</math> , <math>-\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{x}{x-1} \right)</math> |
| − | * [[교차비(cross ratio)|사영기하학과 교차비]], | + | * [[교차비(cross ratio)|사영기하학과 교차비]], [[블로흐-비그너 다이로그(Bloch-Wigner dilogarithm)|Bloch-Wigner dilogarithm]] 항목들을 참조 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==곱셈공식== | |
| − | * 제곱공식 | + | * 제곱공식:<math>\mbox{Li}_ 2(x^2)=2(\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2(-x))</math>:<math>\frac{1}{2}\mbox{Li}_ 2(x^2)=\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2(-x)</math> |
| − | * 일반적인 곱셈공식 | + | * 일반적인 곱셈공식:<math>\frac{1}{n} \operatorname{Li}_ 2(z^n) = \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}\operatorname{Li}_ 2\left(e^{2\pi i k/n}z \right)</math> |
| − | * 실수부와 허수부에 대한 덧셈공식 | + | * 실수부와 허수부에 대한 덧셈공식:<math>f(\theta)=\mathfrak{R}(\operatorname{Li}_ 2(e^{i\theta}))=\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\cos n\theta}{n^2}=\frac{\pi^2}{6}-\frac{\theta(2\pi-\theta)}{4}</math>:<math>Cl_ 2(\theta)=\mathfrak{I}(\operatorname{Li}_ 2(e^{i\theta}))=\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\sin n\theta}{n^2}</math> 다음 덧셈공식을 만족시킴:<math>f(n\theta)=n\sum_{k=0}^{n-1}f(\theta+\frac{2k\pi}{n})</math>:<math>Cl_ 2(n\theta)=n\sum_{k=0}^{n-1}Cl_ 2(\theta+\frac{2k\pi}{n})</math> |
* [[로바체프스키 함수|로바체프스키와 클라우센 함수]]의 덧셈공식 참조 | * [[로바체프스키 함수|로바체프스키와 클라우센 함수]]의 덧셈공식 참조 | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==5항 관계식 (5-term relation)== | |
| − | * 5항 | + | * 5항 관계식은 다이로그 함수의 가장 중요한 항등식의 하나이다.:<math>\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2(y)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{1-x}{1-xy} \right)+\mbox{Li}_ 2(1-xy)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{1-y}{1-xy} \right)=\frac{\pi^2}{2}-\log(x)\log(1-x)-\log(y)\log(1-y)+\log (\frac{1-x}{1-xy})\log (\frac{1-y}{1-xy})</math> |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[5항 관계식 (5-term relation)]] 항목 참조 |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Special values== | |
| − | + | * 다음 여덟 경우만이 알려져 있으며, 이것이 모든 가능한 경우라고 추측된다 | |
| − | |||
| − | * 다음 여덟 | ||
<math>\mbox{Li}_{2}(0)=0</math> | <math>\mbox{Li}_{2}(0)=0</math> | ||
| 102번째 줄: | 95번째 줄: | ||
<math>\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{1-\sqrt{5}}{2})=-\frac{\pi^2}{15}+\frac{1}{2}\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})</math> | <math>\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{1-\sqrt{5}}{2})=-\frac{\pi^2}{15}+\frac{1}{2}\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})</math> | ||
| − | <math>\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{-1-\sqrt{5}}{2})=-\frac{\pi^2}{10} | + | <math>\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{-1-\sqrt{5}}{2})=-\frac{\pi^2}{10}-\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})</math> |
| + | * 구체적인 계산은 [[다이로그 함수의 special value 계산]] 항목 참조 | ||
* [[황금비]] | * [[황금비]] | ||
| − | + | ==다이로그 항등식== | |
| − | + | * 다이로그 함수를 약간 변형한 [[로저스 다이로그 함수 (Rogers' dilogarithm)|로저스 다이로그 함수 (Roger's dilogarithm)]]:<math>L(x)=\operatorname{Li}_ 2(x)+\frac{1}{2}\log x\log (1-x)=-\frac{1}{2}\int_{0}^{x}\frac{\log(1-y)}{y}+\frac{\log(1-y)}{1-y}dy</math> | |
| + | * 대수적수 <math>x_i</math>와 유리수 <math>c</math>에 대한 다음과 같은 형태의 항등식을 다이로그 항등식이라 한다:<math>\sum_{i=1}^{N}L(x_i)=cL(1)</math> | ||
| + | * 모든 다이로그 항등식을 5항 관계식을 통하여 이해할 수 있는지의 여부는 다이로그 함수에 대한 중요한 미해결 문제이다 | ||
| + | * [[다이로그 항등식 (dilogarithm identities)]] 항목 참조 | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Pochhammer 기호와의 관계== | |
| − | |||
| − | <math>\ | + | * [[Pochhammer 기호와 캐츠(Kac) 기호|Pochhammer 기호]]:<math>(q)_{n} : =(q;q)_{n}=(1-q)(1-q^2)\cdots(1-q^n)</math> |
| + | * 로그를 취한뒤 적분을 통해 근사하면 다음을 얻는다:<math>\int_{0}^{n}\log (1-q^{t})\,dt=\frac{1}{\log q}\int_{1}^{q^{n}}\log (1-x)\,\frac{dx}{x}=\frac{1}{\log q}(\operatorname{Li}_{2}(1)-\operatorname{Li}_{2}(q^{n}))</math> | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==재미있는 사실== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Don Zagier | * Don Zagier | ||
| 234번째 줄: | 128번째 줄: | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==역사== | |
| + | * 1696 Leibniz | ||
| + | * 1776 Euler | ||
| + | * 1809 W. Spence, an essay on logarithmic transcendents | ||
| + | * 1828 Abel | ||
| + | * 1840 Kummer | ||
* http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&tbs=tl:1&q=dilogarithm | * http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&tbs=tl:1&q=dilogarithm | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[수학사 연표]] |
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==관련된 항목들== | |
| − | |||
* [[황금비]] | * [[황금비]] | ||
* [[리만제타함수|리만제타함수와 리만가설]] | * [[리만제타함수|리만제타함수와 리만가설]] | ||
| 260번째 줄: | 157번째 줄: | ||
* [[정수에서의 리만제타함수의 값]] | * [[정수에서의 리만제타함수의 값]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==수학용어번역== | |
| − | * 제안용어 | + | * 제안용어 |
| − | ** 쌍로그, 이중로그 ?? | + | ** 다이로그, 쌍로그, 이중로그 ?? |
* [http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en%7Cko&q=di http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en|ko&q=di] | * [http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en%7Cko&q=di http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en|ko&q=di] | ||
| − | * [http://mathnet.kaist.ac.kr/mathnet/math_list.php?mode=list&ftype=&fstr= 대한수학회 수학 학술 용어집] | + | * [http://mathnet.kaist.ac.kr/mathnet/math_list.php?mode=list&ftype=&fstr= 대한수학회 수학 학술 용어집] |
| − | ** http://mathnet.kaist.ac.kr/mathnet/math_list.php?mode=list&ftype=eng_term&fstr=di&page=5 | + | ** http://mathnet.kaist.ac.kr/mathnet/math_list.php?mode=list&ftype=eng_term&fstr=di&page=5 |
** http://mathnet.kaist.ac.kr/mathnet/math_list.php?mode=list&ftype=eng_term&fstr=dilogarithm | ** http://mathnet.kaist.ac.kr/mathnet/math_list.php?mode=list&ftype=eng_term&fstr=dilogarithm | ||
| − | * [http://kms.or.kr/home/kor/board/bulletin_list_subject.asp?bulletinid=%7BD6048897-56F9-43D7-8BB6-50B362D1243A%7D&boardname=%BC%F6%C7%D0%BF%EB%BE%EE%C5%E4%B7%D0%B9%E6&globalmenu=7&localmenu=4 | + | * [http://kms.or.kr/home/kor/board/bulletin_list_subject.asp?bulletinid=%7BD6048897-56F9-43D7-8BB6-50B362D1243A%7D&boardname=%BC%F6%C7%D0%BF%EB%BE%EE%C5%E4%B7%D0%B9%E6&globalmenu=7&localmenu=4 대한수학회 수학용어한글화 게시판] |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==매스매티카 파일 및 계산 리소스== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * https://docs.google.com/file/d/0B8XXo8Tve1cxYXZHTWtTSFhHT2M/edit | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==사전 형태의 자료== | |
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polylogarithm | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polylogarithm | ||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dilogarithm | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dilogarithm | ||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiplication_theorem | * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiplication_theorem | ||
| − | * http:// | + | * M. Abramowitz and I. A. Stegun. Handbook of mathematical functions. |
| − | + | ** [http://people.math.sfu.ca/%7Ecbm/aands/page_1004.htm http://people.math.sfu.ca/~cbm/aands/page_1004.htm] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==관련도서== | |
| − | * Frontiers in number theory, physics, and geometry II | + | * Frontiers in number theory, physics, and geometry II |
** Cartier P., Julia B., Moussa P., Vanhove P. | ** Cartier P., Julia B., Moussa P., Vanhove P. | ||
| − | * [http://books.google.com/books?id=u_UVn_iquj0C Structural properties of polylogarithms] | + | * [http://books.google.com/books?id=u_UVn_iquj0C Structural properties of polylogarithms] |
** Leonard Lewin | ** Leonard Lewin | ||
| − | * Polylogarithms and associated functions | + | * Polylogarithms and associated functions |
** Leonard Lewin | ** Leonard Lewin | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==리뷰논문, 에세이, 강의노트== | |
| + | * Don Zagier [http://vod.mathnet.or.kr/sub2_2.php?no=2326&key_year=x&key_name=zagier The dilogarithm in number theory and geometry] | ||
| + | ** 2012년 4월, 동영상 강의 | ||
| + | * [http://www.stephenwolfram.com/publications/recent/specialfunctions/ The History and Future of Special Functions] Stephen Wolfram, 2005 | ||
| + | * Don Zagier [http://maths.dur.ac.uk/%7Edma0hg/dilog.pdf The Dilogarithm Function] | ||
| + | * Anatol N. Kirillov [http://dx.doi.org/10.1143/PTPS.118.61 Dilogarithm identities],Prog.Theor.Phys.Suppl.118:61-142, 1995 | ||
| − | + | ==관련논문== | |
| + | * O’Sullivan, Cormac. “Zeros of the Dilogarithm.” arXiv:1507.07980 [math], July 28, 2015. http://arxiv.org/abs/1507.07980. | ||
| + | * Broadhurst, David. ‘Tests of Conjectures on Multiple Watson Values’. arXiv:1504.08007 [hep-Th], 29 April 2015. http://arxiv.org/abs/1504.08007. | ||
| + | * Leonard C. Maximon [http://www.jstor.org/stable/3560126 The Dilogarithm Function for Complex Argument], Proceedings: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, Vol. 459, No. 2039 (Nov. 8, 2003) | ||
| − | + | [[분류:다이로그]] | |
| − | + | [[분류:특수함수]] | |
| − | * | + | ==메타데이터== |
| − | * | + | ===위키데이터=== |
| + | * ID : [https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q1238449 Q1238449] | ||
| + | ===Spacy 패턴 목록=== | ||
| + | * [{'LEMMA': 'polylogarithm'}] | ||
2021년 2월 17일 (수) 04:01 기준 최신판
개요
- 폴리로그 함수(poylogarithm)의 하나인 special 함수이다.
- 오일러, 로바체프스키, 아벨 등에 의하여 연구되었다.
- 정수론, 대수적 K-이론, 3차원 쌍곡다양체, 등각장론 등 현대수학의 많은 분야에서 중요한 역할을 한다.
- Pochhammer 기호 \((q)_{n} =(q;q)_{n}=(1-q)(1-q^2)\cdots(1-q^n)\) 의 근사식을 구하는 과정에서 자연스럽게 등장한다.
- 모든 다이로그 항등식 (dilogarithm identities)을 5항 관계식을 통하여 이해할 수 있는지의 여부는 다이로그 함수에 대한 중요한 미해결 문제이다
정의
- 다이로그 함수는 복소수 \(|z|<1\)에 대하여 다음과 같이 정의됨\[\operatorname{Li}_ 2(z)= \sum_{n=1}^\infty {z^n \over n^2}\]\[|z|\leq 1\] 에서 고르게 수렴하는 급수이므로, \(|z|\leq 1\)에서 연속
- 다음과 같은 적분으로 정의하면 해석적으로 확장가능\[\operatorname{Li}_ 2(z) = -\int_0^z{{\ln (1-t)}\over t} dt \] for \(z\in \mathbb C-[1,\infty)\)
함수의 그래프
단위원에서의 실수부와 허수부
- \(z=e^{i\theta}\), \(0 \leq \theta \leq 2\pi\) 일 때,\[\operatorname{Li}_ 2(e^{i\theta})= \sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{e^{in\theta}}{n^2}=\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\cos n\theta}{n^2}+i\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\sin n\theta}{n^2}\]\[\mathfrak{R}(\operatorname{Li}_ 2(e^{i\theta}))=\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\cos n\theta}{n^2}=\frac{\pi^2}{6}-\frac{\theta(2\pi-\theta)}{4}\]\[\mathfrak{I}(\operatorname{Li}_ 2(e^{i\theta}))=\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\sin n\theta}{n^2}=Cl_ 2(\theta)\]
- 로바체프스키와 클라우센 함수 항목 참조
여러가지 항등식
- 오일러의 반사공식
\(\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(x \right)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(1-x \right)= \frac{\pi^2}{6}-\ln(x)\ln(1-x)\), \(0<x<1\)
- 반전공식\[\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{1}{x} \right) = -\frac{\pi^2}{6}-\frac{1}{2}\log^2(-x)\]
- 란덴의 항등식
\(\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{-x}{1-x} \right)=-\frac{1}{2}\log^2(1-x)\) 또는
\(\mbox{Li}_ 2(1-x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(1- \frac{1}{x} \right)=-\frac{1}{2}\log^2(x)\)
- 여기에서 다음의 함수들은 초등함수 부분을 무시하면 같다는 것을 알 수 있음\[\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)\],\(\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(\frac{1}{1-x}\right)\), \(\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(1- \frac{1}{x} \right)\), \(-\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{1}{x} \right)\),\(-\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left(1-x \right)\) , \(-\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{x}{x-1} \right)\)
- 사영기하학과 교차비, Bloch-Wigner dilogarithm 항목들을 참조
곱셈공식
- 제곱공식\[\mbox{Li}_ 2(x^2)=2(\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2(-x))\]\[\frac{1}{2}\mbox{Li}_ 2(x^2)=\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2(-x)\]
- 일반적인 곱셈공식\[\frac{1}{n} \operatorname{Li}_ 2(z^n) = \sum_{k=0}^{n-1}\operatorname{Li}_ 2\left(e^{2\pi i k/n}z \right)\]
- 실수부와 허수부에 대한 덧셈공식\[f(\theta)=\mathfrak{R}(\operatorname{Li}_ 2(e^{i\theta}))=\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\cos n\theta}{n^2}=\frac{\pi^2}{6}-\frac{\theta(2\pi-\theta)}{4}\]\[Cl_ 2(\theta)=\mathfrak{I}(\operatorname{Li}_ 2(e^{i\theta}))=\sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac{\sin n\theta}{n^2}\] 다음 덧셈공식을 만족시킴\[f(n\theta)=n\sum_{k=0}^{n-1}f(\theta+\frac{2k\pi}{n})\]\[Cl_ 2(n\theta)=n\sum_{k=0}^{n-1}Cl_ 2(\theta+\frac{2k\pi}{n})\]
- 로바체프스키와 클라우센 함수의 덧셈공식 참조
5항 관계식 (5-term relation)
- 5항 관계식은 다이로그 함수의 가장 중요한 항등식의 하나이다.\[\mbox{Li}_ 2(x)+\mbox{Li}_ 2(y)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{1-x}{1-xy} \right)+\mbox{Li}_ 2(1-xy)+\mbox{Li}_ 2 \left( \frac{1-y}{1-xy} \right)=\frac{\pi^2}{2}-\log(x)\log(1-x)-\log(y)\log(1-y)+\log (\frac{1-x}{1-xy})\log (\frac{1-y}{1-xy})\]
- 5항 관계식 (5-term relation) 항목 참조
Special values
- 다음 여덟 경우만이 알려져 있으며, 이것이 모든 가능한 경우라고 추측된다
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(0)=0\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(1)=\frac{\pi^2}{6}\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(-1)=-\frac{\pi^2}{12}\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{1}{2})=\frac{\pi^2}{12}-\frac{1}{2}\log^2(2)\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2})=\frac{\pi^2}{15}-\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2})=\frac{\pi^2}{10}-\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{1-\sqrt{5}}{2})=-\frac{\pi^2}{15}+\frac{1}{2}\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})\)
\(\mbox{Li}_{2}(\frac{-1-\sqrt{5}}{2})=-\frac{\pi^2}{10}-\log^2(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2})\)
- 구체적인 계산은 다이로그 함수의 special value 계산 항목 참조
- 황금비
다이로그 항등식
- 다이로그 함수를 약간 변형한 로저스 다이로그 함수 (Roger's dilogarithm)\[L(x)=\operatorname{Li}_ 2(x)+\frac{1}{2}\log x\log (1-x)=-\frac{1}{2}\int_{0}^{x}\frac{\log(1-y)}{y}+\frac{\log(1-y)}{1-y}dy\]
- 대수적수 \(x_i\)와 유리수 \(c\)에 대한 다음과 같은 형태의 항등식을 다이로그 항등식이라 한다\[\sum_{i=1}^{N}L(x_i)=cL(1)\]
- 모든 다이로그 항등식을 5항 관계식을 통하여 이해할 수 있는지의 여부는 다이로그 함수에 대한 중요한 미해결 문제이다
- 다이로그 항등식 (dilogarithm identities) 항목 참조
Pochhammer 기호와의 관계
- Pochhammer 기호\[(q)_{n} : =(q;q)_{n}=(1-q)(1-q^2)\cdots(1-q^n)\]
- 로그를 취한뒤 적분을 통해 근사하면 다음을 얻는다\[\int_{0}^{n}\log (1-q^{t})\,dt=\frac{1}{\log q}\int_{1}^{q^{n}}\log (1-x)\,\frac{dx}{x}=\frac{1}{\log q}(\operatorname{Li}_{2}(1)-\operatorname{Li}_{2}(q^{n}))\]
재미있는 사실
- Don Zagier
The dilogarithm is the only mathematical function with a sense of humor.
역사
- 1696 Leibniz
- 1776 Euler
- 1809 W. Spence, an essay on logarithmic transcendents
- 1828 Abel
- 1840 Kummer
- http://www.google.com/search?hl=en&tbs=tl:1&q=dilogarithm
- 수학사 연표
관련된 항목들
수학용어번역
- 제안용어
- 다이로그, 쌍로그, 이중로그 ??
- http://www.google.com/dictionary?langpair=en|ko&q=di
- 대한수학회 수학 학술 용어집
- 대한수학회 수학용어한글화 게시판
매스매티카 파일 및 계산 리소스
사전 형태의 자료
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polylogarithm
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dilogarithm
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiplication_theorem
- M. Abramowitz and I. A. Stegun. Handbook of mathematical functions.
관련도서
- Frontiers in number theory, physics, and geometry II
- Cartier P., Julia B., Moussa P., Vanhove P.
- Structural properties of polylogarithms
- Leonard Lewin
- Polylogarithms and associated functions
- Leonard Lewin
리뷰논문, 에세이, 강의노트
- Don Zagier The dilogarithm in number theory and geometry
- 2012년 4월, 동영상 강의
- The History and Future of Special Functions Stephen Wolfram, 2005
- Don Zagier The Dilogarithm Function
- Anatol N. Kirillov Dilogarithm identities,Prog.Theor.Phys.Suppl.118:61-142, 1995
관련논문
- O’Sullivan, Cormac. “Zeros of the Dilogarithm.” arXiv:1507.07980 [math], July 28, 2015. http://arxiv.org/abs/1507.07980.
- Broadhurst, David. ‘Tests of Conjectures on Multiple Watson Values’. arXiv:1504.08007 [hep-Th], 29 April 2015. http://arxiv.org/abs/1504.08007.
- Leonard C. Maximon The Dilogarithm Function for Complex Argument, Proceedings: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, Vol. 459, No. 2039 (Nov. 8, 2003)
메타데이터
위키데이터
- ID : Q1238449
Spacy 패턴 목록
- [{'LEMMA': 'polylogarithm'}]